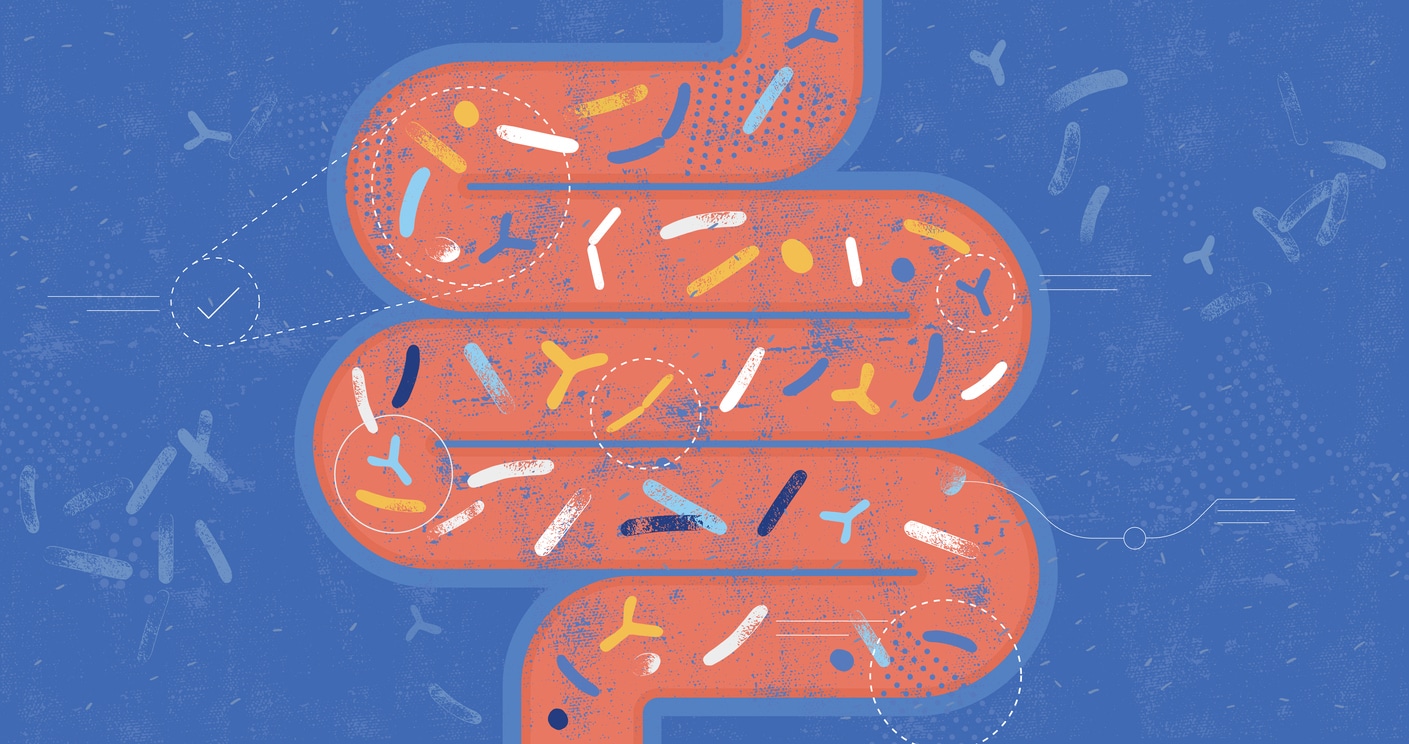
Maintaining a healthy gut is essential for overall well-being. While probiotics have gained significant attention for their role in gut health, another crucial component often overlooked is prebiotics. Prebiotics play a vital role in nourishing the beneficial bacteria in our digestive system, supporting optimal gut function, and promoting overall health. In this article, we will explore what prebiotics are, their benefits, food sources, and how they contribute to a thriving gut ecosystem.
Understanding Prebiotics: The Fuel for Gut Health
- Definition of prebiotics: Prebiotics are non-digestible fibers that serve as a food source for beneficial bacteria in the gut. Unlike probiotics, which are live bacteria, prebiotics are indigestible by humans and instead pass through the digestive system to reach the large intestine, where they are fermented by gut bacteria.
- The role of prebiotics: Prebiotics provide nourishment and promote the growth and activity of beneficial bacteria, such as Bifidobacteria and Lactobacilli, in the gut. They help maintain a balanced and diverse gut microbiota, which is crucial for digestion, nutrient absorption, immune function, and overall health.
Benefits of Prebiotics for Gut Health
- Improved digestion and nutrient absorption: Prebiotics enhance the growth of beneficial bacteria, which aid in the digestion and absorption of nutrients. They contribute to the breakdown of dietary fibers, promote the production of short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs), and enhance the absorption of minerals like calcium and magnesium.
- Enhanced immune function: A healthy gut microbiota plays a significant role in immune system function. Prebiotics support the growth of beneficial bacteria that help regulate the immune response, reduce inflammation, and enhance immune defense against pathogens.
- Reduced risk of gastrointestinal disorders: Prebiotics have been associated with a decreased risk of gastrointestinal disorders, such as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), and constipation. They help regulate bowel movements, improve gut motility, and maintain a healthy intestinal barrier function.
- Mental health benefits: Emerging research suggests that the gut-brain axis, the bidirectional communication between the gut and the brain, plays a role in mental health. Prebiotics contribute to a healthy gut microbiome, which may positively influence mental well-being and help reduce symptoms of anxiety and depression.
Food Sources of Prebiotics
- Inulin-rich foods: Inulin is a type of prebiotic fiber found in various plant-based foods. Some excellent sources of inulin include chicory root, Jerusalem artichokes, onions, garlic, leeks, asparagus, and bananas.
- Fructooligosaccharides (FOS): FOS is another type of prebiotic fiber that supports the growth of beneficial bacteria. Foods high in FOS include bananas, onions, garlic, leeks, asparagus, chicory root, and wheat bran.
- Resistant starch: Resistant starch is a prebiotic that resists digestion in the small intestine and reaches the large intestine intact. Good sources of resistant starch include undercooked potatoes, green bananas, legumes (such as lentils and chickpeas), and whole grains.
- Other sources: Prebiotic fibers can also be found in oats, barley, flaxseeds, seaweed, apples, berries, and certain nuts and seeds.
Supplementing with Prebiotics
While obtaining prebiotics from whole foods is ideal, some individuals may benefit from prebiotic supplements, especially if their dietary intake is insufficient. When considering prebiotic supplements, keep the following in mind:
- Consultation with a healthcare professional: Before starting any supplements, it is advisable to consult with a healthcare professional, such as a registered dietitian or a doctor, to ensure it is appropriate for your individual health needs.
- Selecting reputable brands: Choose prebiotic supplements from reputable brands that have undergone rigorous quality testing and adhere to industry standards.
- Start with small doses: Begin with a lower dosage to assess tolerance and gradually increase as needed. Excessive consumption of prebiotic supplements may cause digestive discomfort, including bloating and gas.
- Combining prebiotics with probiotics: Prebiotics and probiotics work synergistically. Consider incorporating a combination of prebiotic and probiotic supplements to support a healthy gut ecosystem.
Ready to Learn More?
Nurturing your gut health is a crucial step toward overall well-being, and understanding the importance of prebiotics is key in this journey. By incorporating prebiotic-rich foods into your diet and considering prebiotic supplements when necessary, you can support the growth of beneficial gut bacteria and promote a thriving gut ecosystem.
If you're seeking expert guidance and personalized care for your digestive health, Northeast Digestive is here to help. With a team of highly skilled gastroenterologists, dietitians, and healthcare professionals, Northeast Digestive is committed to providing comprehensive digestive care and promoting optimal gut health. Contact us today to learn more!