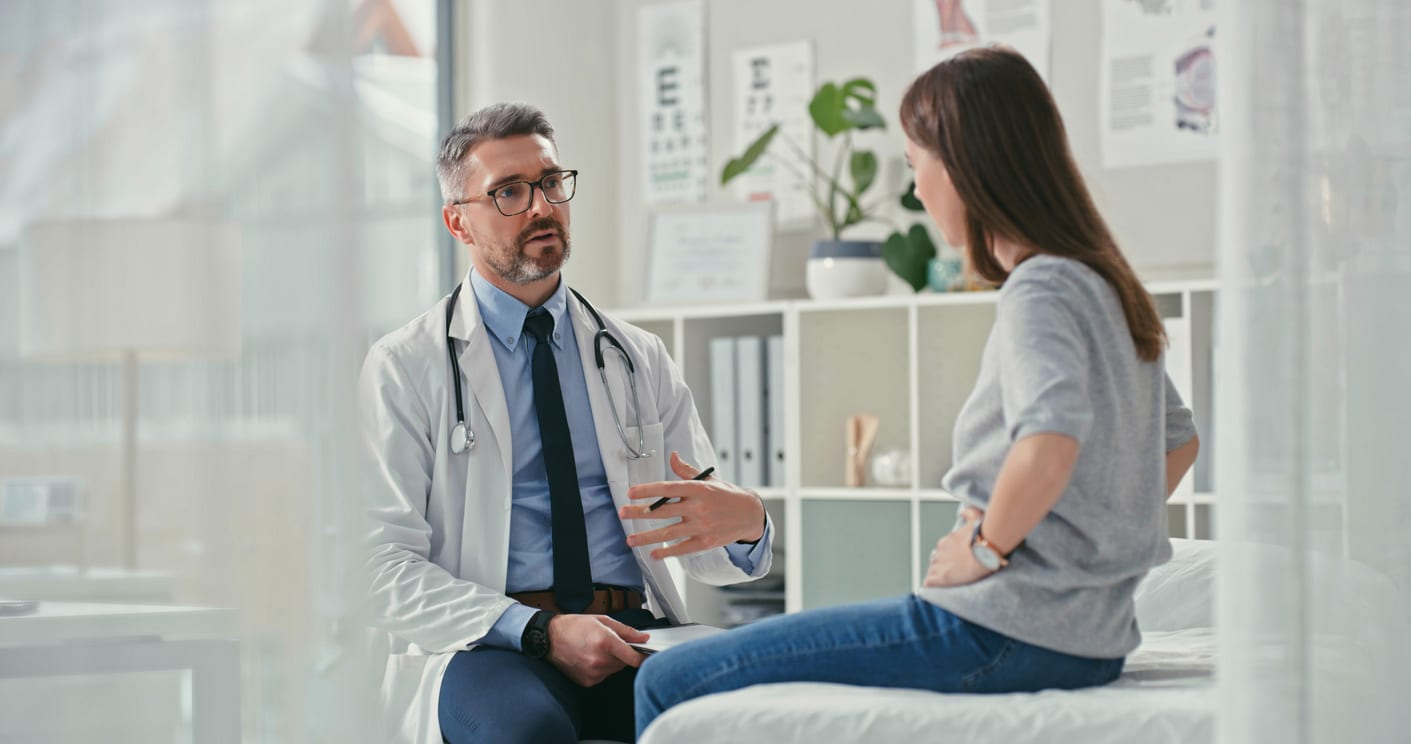
Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) is a common gastrointestinal disorder that affects up to 15% of the world's population. It is a chronic condition that can cause a range of symptoms, including abdominal pain, bloating, constipation, and diarrhea. Although there is no cure for IBS, managing the symptoms can significantly improve the quality of life for those who have it. If you are experiencing symptoms of IBS, it's essential to know when to seek help from a healthcare provider.
When to Seek Medical Attention for IBS
IBS is a chronic condition, and its symptoms may come and go over time. However, if you experience any of the following symptoms for more than six months, you should seek medical attention:
- Abdominal pain and discomfort
- Bloating
- Constipation or diarrhea
- Gas
- Mucus in stool
These symptoms can indicate a range of gastrointestinal conditions, and it's essential to get an accurate diagnosis. Your healthcare provider will examine your medical history and may order laboratory tests and imaging studies to rule out other conditions that may mimic IBS.
IBS is a clinical diagnosis, and there are no specific tests for IBS. Once the diagnosis is established, your healthcare provider will work with you to develop a personalized treatment plan.
Diagnostic Process for IBS
The diagnostic process for IBS typically involves a comprehensive medical history, a physical examination, and laboratory tests. Your healthcare provider may ask you about your symptoms, including their onset, duration, and severity. They may also ask about your family history of gastrointestinal conditions and any medications you are currently taking.
A physical examination may include a thorough abdominal examination to assess for any tenderness or distension. Your healthcare provider may also perform a digital rectal exam to check for any abnormalities.
Laboratory tests may include blood tests, stool tests, and imaging studies such as a colonoscopy or upper endoscopy. These tests can help rule out other conditions that may mimic IBS.
Treatment Options for IBS
The treatment for IBS is typically personalized and may involve lifestyle modifications, medications, and psychological therapies. Here are some of the treatment options for IBS:
Lifestyle modifications
Dietary changes, stress reduction, and exercise may help manage IBS symptoms. Your healthcare provider may recommend a low FODMAP diet, which eliminates fermentable carbohydrates that may cause bloating and gas.
Medications
Depending on your symptoms, your healthcare provider may prescribe medications such as laxatives, antidiarrheals, and antispasmodics. These medications can help manage symptoms such as diarrhea, constipation, and abdominal pain.
Psychological therapies
Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) and hypnotherapy may help manage the psychological stress associated with IBS. These therapies can help you develop coping strategies and improve your quality of life.
Probiotics
Probiotics are live microorganisms that may help restore the balance of gut bacteria. Some studies have shown that probiotics may help reduce symptoms of IBS, although more research is needed.
Seeking Help for Severe IBS Symptoms
In some cases, IBS symptoms can be severe and may affect your daily life. If you experience the following symptoms, you should seek immediate medical attention:
- Blood in stool
- Unexplained weight loss
- Severe abdominal pain
- Anemia
- Difficulty swallowing
These symptoms may indicate a more severe underlying condition that requires immediate medical attention.
Northeast Digestive Can Help
If you are experiencing IBS symptoms, it's essential to seek help from a healthcare provider. At Northeast Digestive Health Center, our team of gastroenterologists can diagnose and treat IBS. We offer personalized care plans tailored to meet your unique needs. Contact us today to schedule an appointment and get the help you need for IBS.